
hereditary (most common, diagnosed in infants and children).reduced secretion of H+ in distal tubule results inability to maximally acidify the urine.
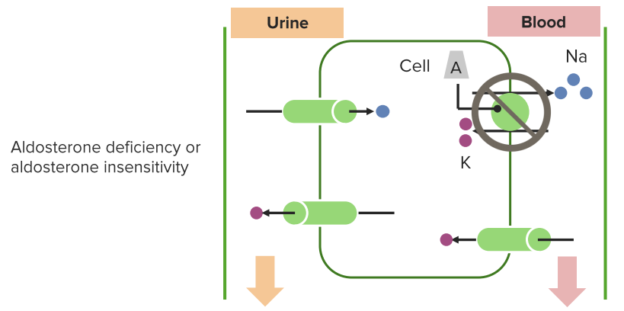
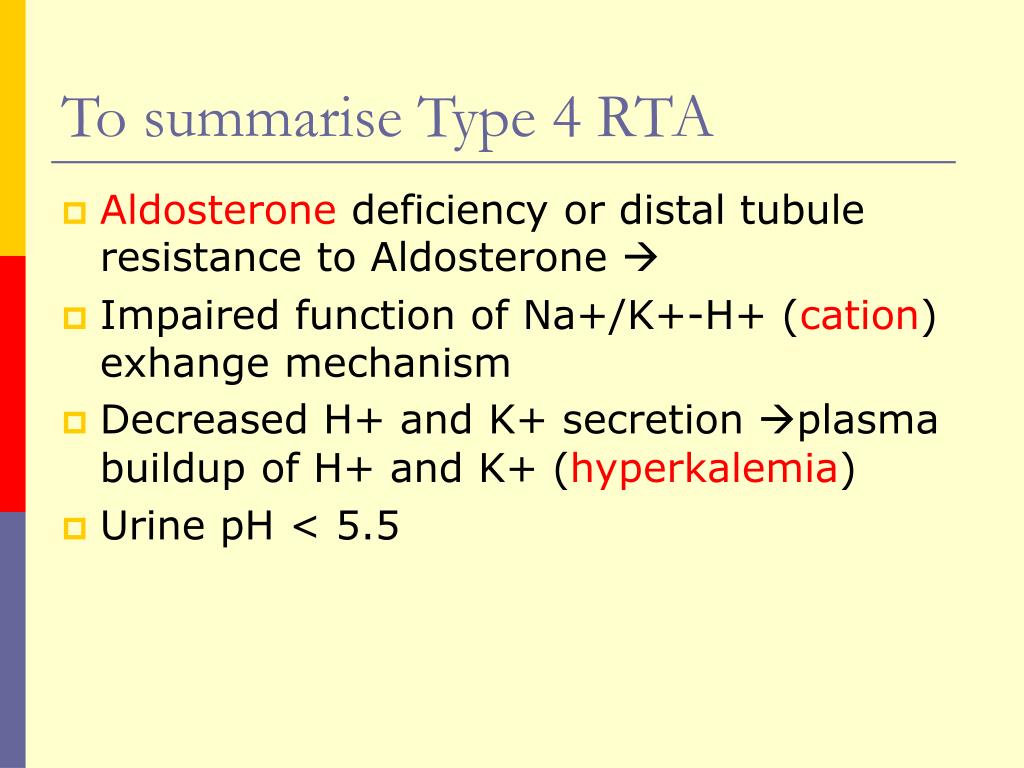
Impaired cation exchange in distal tubule Impaired HCO3 reabsorption in proximal tubule RTA is often detected incidentally through an abnormal blood workup, but some patients present with clinical features such as poor growth, dehydration, or altered mental stateĬOMPARISON OF TYPES OF RENAL TUBULAR ACIDOSIS (RTA).occurs despite a normal or only mildly reduced glomerular filtration rate (GFR).may be incomplete and only develop in the presence of an acid load.results in net acid retention and hyperchloremic normal anion gap metabolic acidosis (NAGMA).primary problem is defective renal acid-base regulation due to impaired ability to acidify the urine and excrete acid.



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
